-
Blockchain supply chain management development has the answer to the issues that have troubled the transportation industry for decades, from dispute resolution to administrative productivity and order monitoring. Let's discuss a couple of these problems.
Logistics Business Issues
Each day, billions of funds get tied up in the logistics industry payment disputes.
Approximately, an organization waits for weeks to months before collecting payments for a standard invoice.
Also, many firms have millions of dollars in their banks tied up, owing to over-reliance on paper transactions.
In the pharmaceutical industry, a large percentage of responsive shipments experience deviations in temperature. Indeed, due to reaching inappropriate temperature ranges, certain shipments never make it past authorities and customs.
As per a study, almost 90 percent of trucking companies own only 6 or fewer trucks. It causes the industry to struggle with meeting demand and supply requirements.
Blockchain for Transportation and Logistics Solutions
New systems allowed by Blockchain would allow for simple document coordination on a decentralized distributed ledger, making physical paperwork largely unnecessary.
Approvals and customs clearance can be faster and more effective by using smart contracts, reducing processing times for goods at customs checkpoints.
Swiss Tech Firm Skycell built refrigerated blockchain-enabled containers that reduced their temperature-deviated rate to less than 0.1 percent.
As the entire network leads to data authentication, Blockchain ensures trustworthy data across the transport and logistics ecosystem.
A recent study found that a simple refrigerated shipment, involving 200+ separate communications, passed through 30+ different organizations.
Any hiccup may cause the container to be held up or lost in these measures.
All of these steps can be registered safely and immutably in real-time with Blockchain.
Traditional tracking systems would not scale, with rising demand for same-day and one-hour delivery services.
A scalable, immediate solution for order monitoring and authentication is offered by blockchain technology.
With Blockchain, a digital ledger could monitor the supply chain for truck parts and used trucks, acting as a sort of remedy for the commercial transport industry.
Also, Read | Driving Efficiency, Security, and Transparency in Logistics with Blockchain
How Blockchain Functions
Blockchain is a distributed ledger storing the history of transactions between parties digitally.
Each block of data on the chain is unique, time-stamped, and encrypted by date, thus, making it unalterable.
In a blockchain, no entity can compromise information or counterfeit it.
Blockchain technology helps businesses implement smart contracts that are computer code hosted on a blockchain. They define and execute the terms of an agreement between parties.

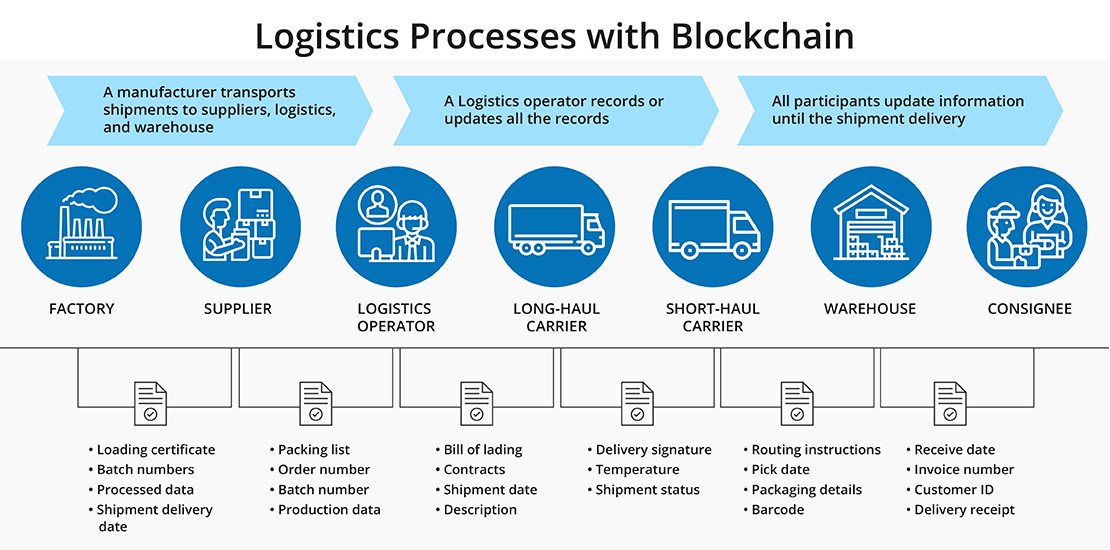
It involves several parties in a typical scenario of shipping goods-shippers.
They include 3PLs, carriers, and consignees. BOLs (bills of lading), invoices, PODs, and more.
Each transaction becomes a permanent record of the ledger that anyone with access to the chain can easily validate.
Network members can validate the block or payload of the transaction using data from a blockchain, creating a transparent and efficient system to manage all documents and transactions involved in the logistics and supply chain process.
Also, Read | Simplifying and Augmenting Logistics Processes with Blockchain
Logistics Advancements with Blockchain Smart Contract Development
Current industry estimates suggest that 10% of all freight invoices contain inaccurate data that leads to disputes in the logistics industry as well as many other process inefficiencies.
This issue is so prevalent that Accenture expects that at least 5 percent of annual freight spending could be reduced by improving invoice accuracy and reducing overpayments in the oil and energy industry alone.
Over the entire logistics and settlement process, including trade finance, Blockchain has the significant potential to increase efficiency and help resolve disputes in the logistics industry.
This information can enable smart contract solutions as digitized documents and real-time shipment data become embedded in blockchain-based systems.
The moment parties involved in a contract meet conditions, smart contracts can automate commercial processes.
A Real-World Example
In the logistics industry, one of the first startups to pursue such a smart contract application is ShipChain.
ShipChain is an early-stage company that has developed a comprehensive blockchain-based system to monitor and trace a product from the moment it leaves the factory on the doorstep of the customer to final delivery.
The system encompasses all freight methods, and there are plans to include an open-architecture API.
It will integrate with current software for freight management.
An immutable distributed ledger technology-powered database records all relevant supply chain information. Further, it executes smart contracts that take action once participants meet predefined conditions.
For example, it can include payment delivery as soon as there's a confirmation of the successful delivery of a shipment in transit.
The platform's tokens called SHIP tokens prove to be a significant aspect of settlement process automation.
On the platform, participants can use these tokens for various activities, including paying for freight services and settling transactions.
A few Use Cases of Blockchain in Logistics
A few of the most prevalent blockchain use cases for the logistics industry are poised to transform it.
Integrating with IoT
In this case, blockchain for logistics, in combination with the Internet of Things (IoT), can enable even smarter logistics contracts.
For instance, a connected pallet can automatically transmit confirmation with information. It will store data about the delivery time as well as goods conditions to the blockchain-based system upon delivery.
The device will then validate the delivery automatically. It will check if the goods delivery is in compliance with negotiated conditions, including temperature, humidity, etc.
After validation, it will release accurate payments to appropriate parties, thus, improving reliability and credibility significantly.
In the IoT context, blockchain technology can simplify machine-to-machine payments. For instance, connected machines negotiate and execute prices based on the logistics activities performed.
The digitization of letters of credit (L/C) to expedite planning and execution is another example of smart contracts in logistics.
It is a process that usually appears to take from days to weeks.
Also, Read | Making Logistics Processes Efficient with Blockchain Applications
For more information about how blockchain technology integration for logistics solutions caters to today's increasing business and consumer demand, connect with our blockchain development experts.

Our Offices
INDIA
Emaar Digital Greens, Sector 61,
Gurugram, Haryana
122011.
Welldone Tech Park,
Sector 48, Sohna road,
Gurugram, Haryana
122018.













