-
Blockchain is a friction-less platform that is currently gaining popularity across various industries, including financial services, BFSI, retail, healthcare, manufacturing, and more. For staying competitive and meeting the ever-growing consumer needs, market leaders across sectors are exploring technology solutions. The payment processing industry is no exception. Recently, due to the potential of blockchain solutions development to substitute intermediaries and enable faster digital payment processing, technology has witnessed a growing number of advocates in the industry.
However, the question arises that how businesses can seamlessly implement blockchain fintech development to reap long-term benefits in payment processing. This article discusses crucial principles about blockchain implementation in payment processing. Discover how it enables the processing of payments in a faster, secure, and digitized way.
Traditional Payment System Challenges
The existing payment infrastructure is largely message-based and relies on multi-party file exchange. A standard cross-border lifecycle of non-euro payments requires processing through multiple phases. It takes from weeks to days to complete. For instance, because of this delay, it requires a business initiating a payment to monitor its bank account or bank account statement to get its clearance status.
Blockchain Features for Payment Processing Advancements
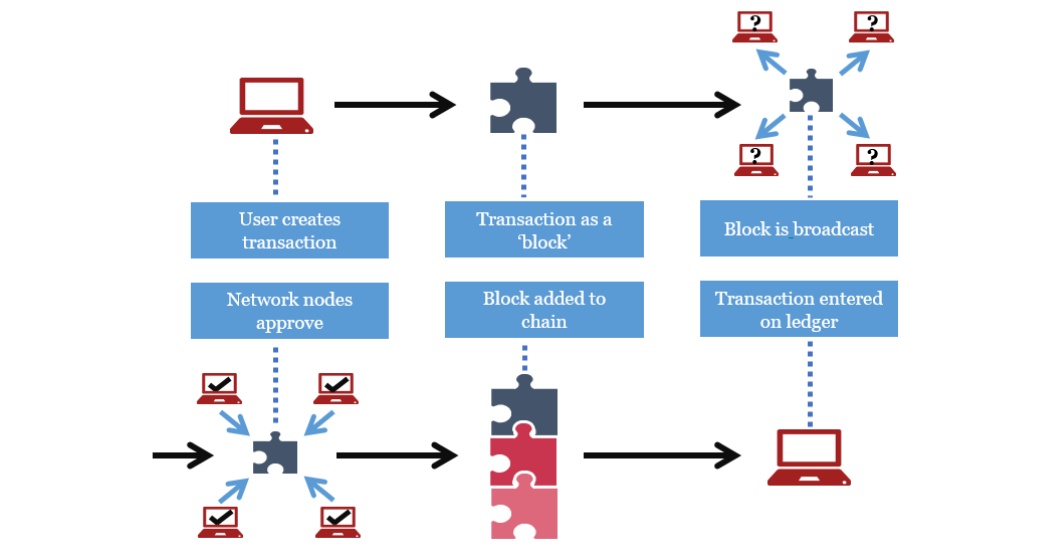
Source: PWC
Peer-to-Peer Transactions Model
Blockchain is a protocol that runs on top of the Internet, on a peer-to-peer network of computers, all running a real-time data exchange protocol. From the perspective of global payment services, if payment parties are part of such a scheme, an exchange of payment information (such as clearing & settlement details) will occur in real-time, reducing lags in payment processing & settlement times. It addresses one of the issues with global payments. Additionally, it does not charge anything. Thus, the transactions do not get correlated with any network transmission rate.
Also, Read | Making Secure Online Payments with Blockchain-Based Crypto Wallets
Distributed Ledger Technology
Blockchain is a decentralized digital ledger that facilitates the creation of an immutable historical transaction record. The database gets simultaneously stored across several computers that are part of the network.
It ensures a shared view of the same data across the network to all permissioned identities. It removes the introduction of lengthy and time-consuming reconciliation procedures by banks to ensure transaction integrity across payment processing networks. Also, it helps to enhance customer service by rapidly supplying them with valuable information: specific timings, numbers, charges, and fees received by each party in a transfer of funds.
Cryptographic Mechanisms
For protection from tampering, blockchain technology cryptographically signs the transactions signed, making them secure. Also, in the ledger, an auditable trail of all the transactions is always available. These features reduce the need for global payments from a trusted middleman or intermediary banks that financial institutions require. The use of an intermediary contributes to the expense and creates a pause in the processing of payments.
Data Security and Privacy
Unlike "permission-less" blockchain networks, where transaction information is made accessible from a data privacy point of view to anyone in the network, rendering it unsuitable for controlled financial institutions.' Permitted' blockchain platforms such as Hyperledger, Ethereum & Corda keep financial institutions' data privacy rules, information protection & regulatory requirements in mind. The shared ledger is fortified with access control in the approved blockchain to ensure that transactions between parties are available only to them.
Smart Contract Solutions
A smart contract is a piece of software that includes a pre-defined set of rules. It enforces them during the transaction phase to ensure that all requirements meet and complete the transaction, as specified by the business process. Any business validation to be carried out outside the payment system from a payment perspective, such as the permissibility of a certain form of transactions or potential duplicate checks, can be done by a smart contract solution from a payment perspective.
Trust-Less Governance Model
The consensus protocol ensures a transaction's credibility and continuity. By executing a smart contract code, stakeholders can validate a transaction. When one or more than one node decides that the transaction is true and unique, the network reaches a consensus. It essentially ensures no forgery or double-spending of funds by engaging in payment services.
Blockchain Applications | Payment Processing Systems/Solutions
Advanced International Reconciliation
SWIFT completed a proof of concept (PoC) with 34 global banks to determine whether Nostro reconciliation could be used with Blockchain. Nostro/Vostro accounts where a bank in a few countries does not directly offer services. It does so through a correspondent bank. The PoC concluded that, if implemented globally by all the participating banks, blockchain could effectively facilitate automated real-time liquidity tracking and reconciliation.
Also, Read | Fast, Secure, and Efficient Digital Payment Solutions with Blockchain
Frictionless Card Payment Solutions
Card payments for shoppers are a convenient, cashless payment choice, but merchants receive a high transaction fee. There are intermediaries, including acquirers, payment gateways, exchanges (Visa/Master), and issuers (cardholders' bank). There will be no need for too many authoritative bodies because there is no central authority in a blockchain network. It assists retailers to pay less for service costs and transaction fees and provide consumers higher discounts in exchange.
Secure and Fast Cross-Border Payment Processing
When traveling from one country to another, cross-border payments have to move through many banks. It boosts the fees involved in making them. Mastercard has developed a blockchain-based solution that connects the sending and receiving bank directly. It does not involve intermediaries with this settlement network. They can achieve this without using any cryptocurrency, as well as enable fund transfers as fiat currencies. Likewise, FinTech provider R3 is working with 22 banks to develop a solution for real-time international payments that use Distributed Ledgers to allow cross-border payments that are quick, efficient, and cost-effective.
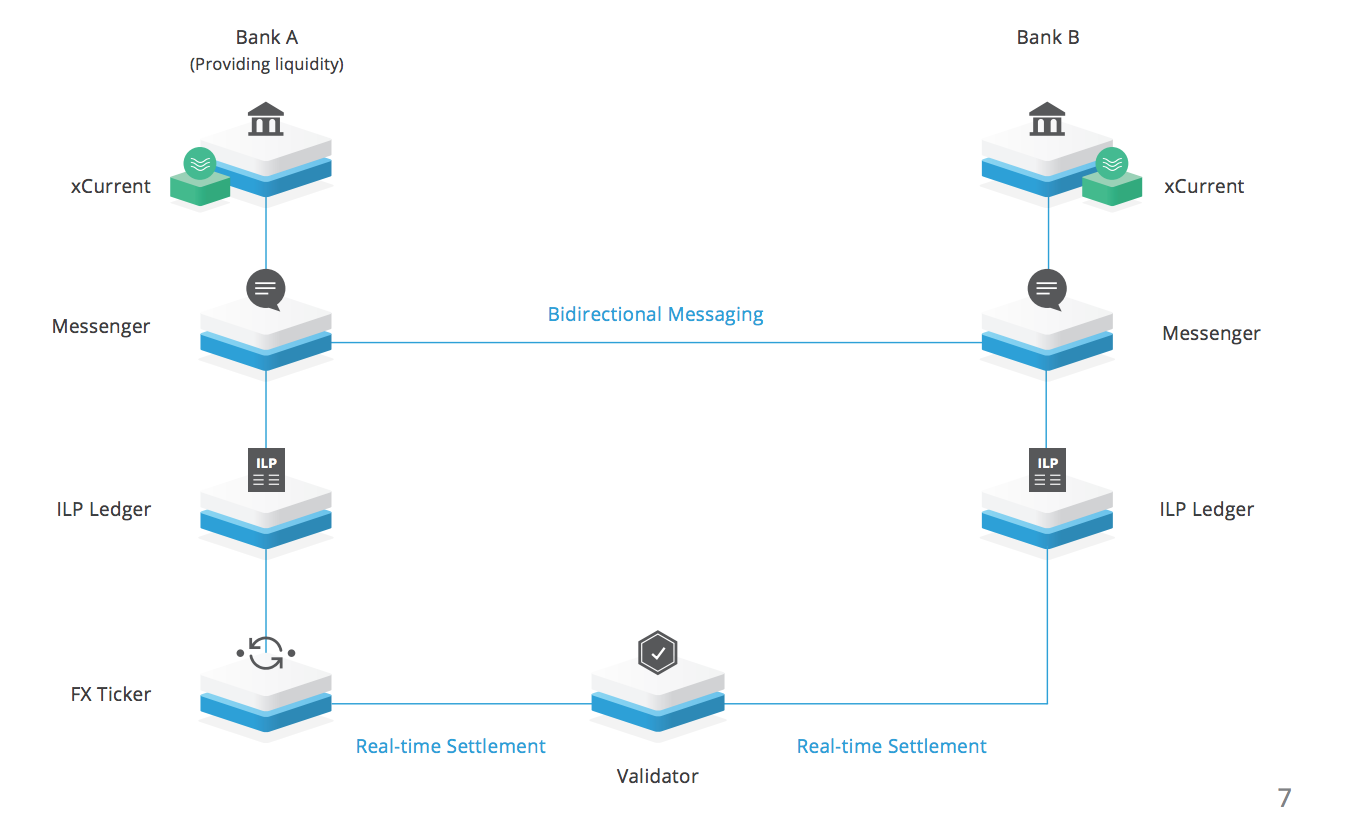
Source: Ripple (xCurrent)
Simplified Trade Financing
Multiple intermediary banks oversee trade finance between a buyer and a seller, whether domestic or intermediary, using financial products. The functionality provided by blockchain technology is smart contracts for trade finance. These are self-executing contracts, while the terms of exchange remain on the blockchain as codes. These execute payments automatically when parties fulfill particular conditions. The receipt of a shipment of items may be an indication of a situation.
Conclusion
Digital currencies will become more common. We already see a few digital currencies emerging globally to power cross-border transactions, some backed by central banks, some not. Universal tokens, most likely secure coins. A single norm would arise, maybe. Other blockchains with slower transactions can find use as value stores or objects of speculation. Let's connect with our blockchain experts to discuss a future project.

Our Offices
INDIA
Emaar Digital Greens, Sector 61,
Gurugram, Haryana
122011.
Welldone Tech Park,
Sector 48, Sohna road,
Gurugram, Haryana
122018.













